- Published on
Ethereum - 9 years old for Crypto's “big brother”
- Authors

- Name
- Administrator
- @airdropdecks
Ethereum, first introduced in 2015, has evolved from a mere idea into a global blockchain platform. With a mission to provide a decentralized system, Ethereum lays the foundation for the explosion of DeFi, NFTs, and Web3.
2015: Genesis block is born
Ethereum was proposed in late 2013 by Vitalik Buterin, a Russian-Canadian programmer. Vitalik's idea is to build a blockchain platform that not only performs transactions like Bitcoin, but is also capable of programming through smart contracts.
- Whitepaper and Crowdfunding (2014)The first Ethereum whitepaper was published by Vitalik in 2014, explaining the goals and structure of the network. To raise funds, the founding team held an ICO (Initial Coin Offering), which sold 60 million ETH and raised about $18 million — one of the most successful ICOs of the time.
- The Genesis Block (2015):Ethereum officially went live on July 30, 2015 with the first update called “Frontier”, marking the introduction of the Genesis block at 3:26:13 AM GMT and the Ethereum network.

2015-2016: First steps in development
Frontier Demo
Ethereum started with an experiment called Frontier (2015), which allowed developers to build and deploy smart contracts. Although it was in its infancy, it was:
- Activate the first Ethereum mainnet network.
- Supports basic smart contracts and ETH transactions.
- Testing the Proof-of-Work (PoW) mining mechanism for maintaining network operations.
Homestead Upgrade
Next, the Homestead update (2016) improved performance and security, making the network more stable.
- Increased Stability and Safety:Homestead fixes bugs in Frontier and improves network performance.
- Improving the developer experience: Supports multiple tools that make decentralized application deployments (dApps) and smart contracts easier.
- Transition of official status: Homestead marks the transition from experimental to formal use, building trust in the community.
2016: The DAO crash and Ethereum's first historical turning point
In 2016, Ethereum faced its biggest challenge since its inception when The DAO, a prominent decentralized governance project of the time, was seriously hacked. The crash occurred not due to a bug in the Ethereum protocol, but due to a flaw in The DAO's smart contract code.
However, since The DAO controls up to 15% of the total ETH supply, the incident severely impacted the network, threatening the community's trust in Ethereum and putting enormous pressure on the value of ETH.
In June 2016, an attacker exploited The DAO's vulnerability, withdrawing 3.6 million ETH (roughly $50 million at the time) into a “child DAO” — a smart child contract. The event quickly became the focus of the crisis, as the community faced the question of how to handle this situation in order to protect networks and investors.

Many solutions are offered, including a proposal from Ethereum co-founder Vitalik Buterin. Among them, the most favored solution is to perform a hard fork to reverse the attacker's transactions, thereby recovering the lost ETH and protecting the interests of The DAO investors.
The hard fork received approval from 85% of the community, but also encountered opposition from a minority group. The group argues that The DAO's error is not the responsibility of the Ethereum protocol and that changing the blockchain would disrupt immutability — a core principle of blockchain technology. They decided to continue to maintain the old chain, later known as Ethereum Classic (ETC).
As a result, the Ethereum community splits into two branches:
- Ethereum Classic (ETC): Maintain the original blockchain, where The DAO attack still exists.
- Ethereum (ETH): Perform a hard fork to recover the lost ETH and become the main chain of the current Ethereum network.
The DAO incident is not only an important lesson in the risks of smart contracts, but also a turning point in making Ethereum more mature. Resolving this crisis not only strengthens Ethereum's long-term vision, but also shapes how the network responds to future challenges.
At the end of 2016, Ethereum continued to implement two more hard forks:
- Tangerine Whistle:Fixes vulnerabilities and improves network protection against denial of service (DoS) attacks.
- Spurious Dragon:Enhance security and remove invalid accounts created in previous attacks.
2017-2019: Ethereum's Leap Forward
The boom of ICOs
Ethereum becomes the main platform for projects raising funds through ICOs thanks to the ERC-20 token standard. ICOs have leveraged Ethereum as a fundraising tool, with prominent projects such as Filecoin, Tezos, and EOS raising hundreds of millions of dollars. ICOs bring massive funding to blockchain projects, giving a strong growth impetus to the Ethereum ecosystem.
However, ICO wave It also brings a lot of risk. Many fraudulent projects emerge, taking advantage of investors' ignorance to raise capital without an actual product. This led to a lot of criticism and negatively affected Ethereum's reputation.
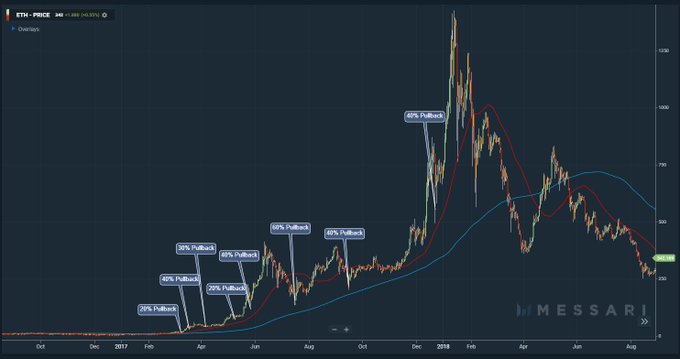
Historical Bullish Bullish
2017 also saw a spectacular rise in the price of ETH, reflecting the huge investor interest in blockchain and Ethereum. ETH's price peaked near $1,400 in early 2018, marking an important turning point in Ethereum's history. This not only confirms the value of Ethereum, but also fuels the development of DeFi and decentralized applications.
Metropolis: Byzantium Upgrade (October 2017)
Ethereum has made the first major upgrade in its Metropolis roadmap called Byzantium. Notable changes in Byzantium include:
- Reduced mining rewards: The reward per block is reduced from 5 ETH to 3 ETH, in order to control inflation and adjust the value of ETH according to real demand, adopted by EIP 649.
- Postpone the “difficulty bomb”:The difficulty bomb (the mechanism that makes mining more and more difficult over time) has been delayed for another year, giving Ethereum time to prepare for the transition to Proof-of-Stake (PoS).
- Supports calls that do not change status: Byzantium allows the execution of stateless calls between smart contracts, increasing flexibility and efficiency in transaction processing.
- Add new encryption methods: The upgrade provides cryptographic tools that support layer 2 expansion, paving the way for solutions such as zk-Snarks and Plasma.
The Byzantium upgrade is an important start in improving the Ethereum network, while 2019 upgrades such as Constantinople and Istanbul have brought Ethereum closer to its goal of scalability, security and efficiency.
Constantinople (February 2019):
- Reduce block rewards: From 3 ETH to 2 ETH, tighter control of ETH supply.
- Improved gas costs: EIPs such as EIP-1052 and EIP-1014 reduce the cost of executing smart contracts and increase efficiency when interacting between contracts.
- Prepare for PoS: Lays a solid foundation for the transition to the PoS mechanism.
Istanbul (December 2019):
- Increased scalability: Supports Layer 2 technologies such as zk-SNARKS and Plasma, increasing transaction processing.
- Increased compatibility: Ethereum becomes better interoperable with other blockchains such as Zcash.
- Reduce gas costs: Some EIPs, including EIP-2028, help reduce transaction costs, expand applications for dApps and DeFi.
Foundations for DeFi
The 2017-2019 period is the beginning of decentralized finance on Ethereum, with important advances but not yet a strong boom. MakerDAO, launched in late 2017, marked a turning point with the introduction of the DAI stablecoin, the first decentralized stablecoin to be priced at USD through ETH collateral. This is an important step in creating secure financial protocols that do not require intermediaries.
In addition, Uniswap, with its AMM (Automated Market Maker) model, also appeared in 2018. This protocol not only provides a way to trade tokens directly on the blockchain, but also lays the foundation for modern decentralized exchanges (DEXs).
Compound, launched the same year, offers a decentralized lending and borrowing solution, helping users optimize assets without depending on traditional financial institutions.

By 2019, DeFi began to expand more with the development of existing protocols and the emergence of new names. Uniswap releases version v2, which improves trading capabilities and supports more token pairs. Synthetix launches, which provides a solution to create synthetic assets such as gold and stocks on the blockchain, expanding Ethereum's scope of application.
However, this period also faces challenges such as high gas costs due to the increased demand for Ethereum usage, security risks from new protocols, and the complexity of the DeFi approach.
Even so, DeFi in 2017-2019 laid a solid foundation, putting Ethereum at the center of decentralized finance, paving the way for a strong boom in 2020.
2020-2022: Conversion to Ethereum 2.0
Launch of Beacon Chain (December 2020)
The implementation of Beacon Chain in December 2020 marks an important and fundamental start in Ethereum's long-term development path. This is the network's first attempt at transitioning from a Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanism, which is energy-intensive, to Proof of Stake (PoS), a more sustainable and efficient solution.
Instead of applying directly on the main chain, Ethereum chooses to operate the Beacon Chain as a standalone system, running parallel to the main network. This allows the network to test and ensure stability and safety before comprehensive integration of PoS into the main chain.
The implementation of Beacon Chain not only helps test and improve the system, but also lays a solid foundation for future major upgrades, highlighted by The Merge event, where Ethereum officially merges Beacon Chain with the main chain in 2022. By the end of 2022, total ETH staking had surpassed the 16 million ETH mark, demonstrating strong community confidence in the PoS mechanism and the security of the network.

2020 also saw the introduction of a potentially new concept: liquid staking. This solution allows users to participate in ETH staking to secure the PoS network without being bound by a minimum requirement of 32 ETH or loss of asset liquidity.
One of the pioneering projects in this field is Lido, which was launched just three weeks after Beacon Chain officially went live. Lido quickly dominated the liquid staking market thanks to its ability to deliver a smooth user experience and a high level of security.
Beacon Chain not only opens Ethereum's journey of innovation, but also sets the stage for important improvements, helping the network grow sustainably, expand its reach and increase trust from the global community.
Following Beacon Chain, Ethereum continues to roll out many major upgrades to improve the cost, performance, and scalability of the network:
- Berlin Upgrade (April 2021):Optimize gas costs and increase efficiency for complex transactions, supporting smart contract development.
- London Upgrade (August 2021): Introducing EIP-1559, changing the gas fee mechanism with a fixed “base fee”, creating transparency and reducing the supply of ETH thanks to the transaction fee burning mechanism.
Evolution of Layer 2 (2021)
In 2021, the layer 2 ecosystem on Ethereum thrived, playing a key role in addressing high gas charges and network congestion, two major challenges for Ethereum.
Technologies such as Optimistic Rollups and ZK-Rollups offer efficient scalability solutions, allowing for batch processing of off-chain transactions at a lower cost before recording results on Ethereum. At the same time, layer 2 platforms such as Arbitrum and Optimism have attracted many DeFi projects and users thanks to their ability to improve transaction speeds and reduce costs.
These improvements not only help Ethereum maintain its leading position in the DeFi space, but also enhance the ecosystem's reach, despite competition from layer 1 blockchains such as Solana and Avalanche.
Thanks to Layer 2, Ethereum continues to consolidate its role as the center of decentralized finance while expanding the scope of applications and optimizing the user experience.
The Merge: Merge Ethereum and Beacon Chain (September 2022)
The Merge event in September 2022 marked a significant milestone in Ethereum's history, when the network officially merged with Beacon Chain, completing the transition. This is one of the most complex and influential technical upgrades in the blockchain industry, helping Ethereum reduce energy consumption by 99.95%, from the equivalent of a small nation's electricity consumption to just the size of a medium-sized city.
The Merge not only improves energy efficiency, but also opens up great opportunities in terms of sustainability and scalability. The move to PoS has eliminated the need for miners to use dedicated hardware, instead users can stake ETH to participate in transaction validation and network security. As of the end of 2022, more than 16 million ETH had been staked, or more than 13% of the total ETH supply, indicating strong community confidence in this new system.
In addition to the technical benefits, The Merge also lays the foundation for future major upgrades, including Surge, Verge, and Purge, aimed at improving scalability and reducing transaction costs. This is not only a turning point for Ethereum, but also a testament to the network's ability to innovate and adapt, which continues to maintain its position as the largest blockchain platform for decentralized and DeFi applications.

2023: ETH Withdrawal Enables and Advances with DVT Technology
2023 is a significant milestone for Ethereum, especially with the Shapella (Shangai + Capella) upgrade in April. For the first time since staking launched in 2020, users have been able to withdraw staked ETH.
Contrary to the prediction that this will cause more people to withdraw ETH and depreciate in value, reality shows that ETH staking increased by about 3 million ETH (up 15.5%) in just the first month. This suggests strong trust in the network, which led to months of waiting to activate staking, which was only fully resolved in October.
The staking boom also spurred the development of Distributed Validator Technology (DVT), a technology that better secures the Ethereum network and makes the system more flexible and stable. DVT allows multiple operators to share responsibility for protecting networks, enhancing decentralization, and reducing the risk of incidents.
One of the prominent projects in adopting DVT is SSV Network, with more than 34,000 authenticators and 1.1 million ETH being staked. SSV Network not only enhances security, but also expands decentralized staking capabilities, making the Ethereum network more stable.
2023 will not only be the year that opens the possibility of withdrawing ETH, but also the year of strengthening confidence in Ethereum with important improvements in the security, decentralization and long-term growth of the network.
2024: Blobs and Restaking
2024 brings many improvements focused on the scalability and improvement of Ethereum's staking ecosystem. The first half of the year witnessed upgrade Dencun, a step that reduces transaction costs and improves data processing efficiency on the Ethereum network. These enhancements not only help users save costs, but also facilitate layer 2 solutions such as rollups, enhancing the overall experience of the network.
Another highlight of the year is the development of restaking technology, introduced by EigenLayer. Restaking allows users to stake ETH to not only secure the Ethereum network but also support other networks.

In April, the Restaking Authorization feature was launched, paving the way for the emergence of Actively Validated Services (AVS) services. Projects such as AltLayer, Automata, Eigenda, Hyperlane and many others have successfully deployed on the main network, showing the application potential of restaking technology in enhancing security and interaction between networks.
In addition, liquid restaking has received a lot of interest in the Ethereum community. This technology allows users to stake ETH while still being able to participate in authentication across multiple networks. Typical projects in this area include ether.fi, Puffer, Renzo and Swell, which increase the flexibility and efficiency of staking.
In the summer, Ethereum noted the launch of Symbiotic, a decentralized shared security platform. Symbiotic provides tools for projects and users to collaborate on security transparently, without the need for intermediaries. This is an important step in promoting decentralization and transparency in the network.
2024 shows Ethereum's focus on improving efficiency, reducing costs and expanding staking applications, thereby further consolidating its role in the global blockchain ecosystem.